Importance of standardization in financial messaging for international value transfers
The current cross-border payments landscape is faced with the problem of lack of interoperability and integration between different clearing systems. To address the issue, standardization in the financial messaging is to be achieved because standardization
means richer and more structured data in the international financial messaging which eventually leads to faster and smoother reconciliation and settlement processes. The ISO 20022 standard elaborates on innovating the international payments industry by bringing
harmonization, transparency, speed, flexibility and higher interoperability into the system.
Timeline and use of different financial messaging formats
![]()
Telex message or telegraphic transfer (TT), is an electronic method of fund transfer used before SWIFT for International wire transactions. In relation to the transfer locations and requirements of currency exchange, completion of a telegraphic transfer
may take two to four business days. Telex has the disadvantage of security concerns, slower speed and a non-unified messaging system like SWIFT. This is why Telex messages were prone to too many human errors in the process of translating the sentences used
to describe the transactions.
ISO 7775 messaging standard included the actual messages themselves such as the MT 520 or MT 534 of SWIFT types; however, it takes excessive amount of time and effort to make any changes to these standards. ISO 7775 standard is applicable to the messages
conveyed in writing, by way of forms, telex or data telecommunication. ISO 7775 was highly unstructured and therefore insufficient in providing accurate and complete settlement information in comparison to its successors ISO 15022 and ISO 20022.
In order to prevent the complexities faced with ISO 7775 messages, ISO 15022 standard was developed which does not involve the actual messages but the guidelines and rules to create messages. The aim was to create a more standardized and unified messaging
system with a dictionary of data fields, a syntax and a catalog to be used for the present and future messages to support specific data flows in the financial messaging.
The adoption of ISO 15022 messaging standard was created in 1998 and authorized in 2003 which increased the rates of Straight Through Processing (STP) dramatically. The data dictionary introduced with ISO 15022 enabled better re-use and standardization of
data. Almost 50% of the 20 million financial messages which are transferred via SWIFT each day use ISO 15022 standard.
Although ISO 15022 aimed to increase standardization with a more structured data set, it was still insufficient in terms of the use of different syntaxes and semantics. The MT standard used by ISO 15022 remained limited in analyzing and classifying data
efficiently because of its limited character set and number as well as the unstructured data arrangement. It is highly open to unwanted complications which require manual intervention and time.
The MX standard that ISO 20022 using offers a more structured and automated data in financial messaging.
The standardization in financial messages is achieved with ISO 20022 in addition to the advantages of transparency, flexibility, compliance, resilience, data quality and velocity.
The full adoption of ISO 20022 is delayed to November 2022 by SWIFT.
ISO 20022 migration scope and timeline
Within the scope of ISO 20022 migration, cross-border payments and financial messages of cash management are covered. Therefore, the scope is limited to MT Standards: Category 1, 2 and 9 messages only and the rest of the categories will carry on as they
used to be.
In the migration timeline created by SWIFT, there is a coexistence period of MT and MX messages which is expected to continue for 3 years from November 2022 until November 2025. The coexistence period of MT and MX messages will end after November 2025 and
only MX standard messages will be used and supported for the financial message categories.
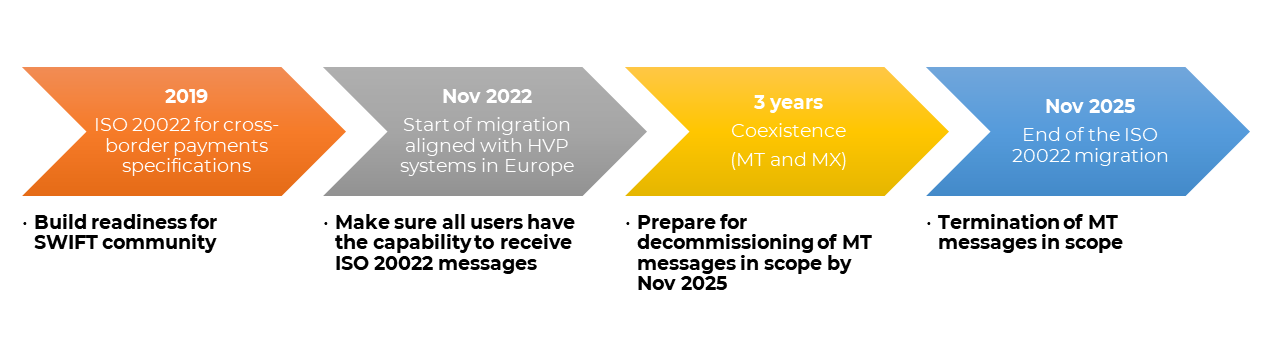
Source: SWIFT ISO 20022 Programme Timeline
Global payments networks that will comply with ISO 20022
SWIFT’s relation to ISO 20022 is extensive and profound. SWIFT took active role in the creation and development process of ISO 20022 specification together with the ISO working group in 2000. In 2004, SWIFT was chosen as the Registration Authority (RA) for
the ISO 20022 standard and was given the responsibility to publish the central repository and maintain the integrity of ISO 20022. More than 85% of the message definitions contained in the IS 20022 catalogue are created by SWIFT.
SWIFT also provides tools and services for those who develop content for ISO 20022 in order to support contributing organizations to conform with the standard. In addition to the tools SWIFT offers, there are other tools and services which are made available
by SWIFT partners and other vendors.
Ripple is a payments network that uses the power of blockchain and digital asset technology, to support financial institutions in improving the speed, cost and reliability of their transactions. Ripple is the first ISO 20022 Standards Body member that focused
on Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). Ripple aims to offer her clients better service via its RippleNet system and its membership to ISO 20022.
Visa DPS is the greatest processor of Visa that processes more than 50% of Visa US Debit and largest number of Visa transactions globally. Visa DPS is using ISO 20022 in the processes of authorization via an API Interface. By adopting ISO 20022 standard,
Visa aims to improve simplicity, flexibility and interoperability within the financial messaging services.
Type of business transactions that will be compatible with ISO 20022
There are specific identifications used in ISO 20022 to define the business areas in the financial messaging. They are mostly related to payments (50%), securities (47%) and trade. Depending on the industry requirements, the areas covered are expanding by
including other fields supporting payments landscape such as bank account management, Forex, cards, debit mandate management etc.
The whole payments chain (end-to-end) is covered by ISO 20022 messages including customer to bank (payment), interbank (payment clearing and settlement) and cash management (reporting).
To improve and facilitate the processes of clearing and settlement of securities, new international and local market infrastructures (MI) have emerged. As the number of trans-border transactions increase day by day, MIs needed to choose a messaging standard
to use in their communication. Most important and eminent ones such as Eurosystem’s renewed securities settlement service TARGET2-Securities (T2S), the US Depository Trust and Clearing Corporation (DTCC) and JASDEC, the Japanese Central Securities Depository
decided on using ISO 20022 as the messaging standard.
Currently, among 75 ISO 20022 messages used for trade area, 50 of them are utilized by FIs to communicate with TSU (Trade Service Utility). TSU basically supports banks in dealing with the supply chain problem and offer elevated financing services for open
account settlement.